Upgrading and Reinstalling
Starting from Kubeflow v0.5, Kubeflow Pipelines persists the pipeline data in permanent storage volumes. Kubeflow Pipelines therefore supports the following capabilities:
-
Reinstall: You can delete a cluster and create a new cluster, specifying the existing storage volumes to retrieve the original data in the new cluster. This guide tells you how to reinstall Kubeflow Pipelines as part of a full Kubeflow deployment.
-
Upgrade (limited support):
The full Kubeflow deployment currently supports upgrading in Alpha status with limited support. Check the following sources for progress updates:
Before you start
This guide tells you how to reinstall Kubeflow Pipelines as part of a full Kubeflow deployment on Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE). See the Kubeflow deployment guide.
Instead of the full Kubeflow deployment, you can use Kubeflow Pipelines Standalone or GCP Hosted ML Pipelines (Alpha), which support different options for upgrading and reinstalling. See the Kubeflow Pipelines installation options.
Kubeflow Pipelines data storage
Kubeflow Pipelines creates and manages the following data related to your machine learning pipeline:
- Metadata: Experiments, jobs, runs, etc. Kubeflow Pipelines stores the pipeline metadata in a MySQL database.
- Artifacts: Pipeline packages, metrics, views, etc. Kubeflow Pipelines stores the artifacts in a Minio server.
Kubeflow Pipelines uses the Kubernetes PersistentVolume (PV) subsystem to provision the MySQL database and the Minio server. On GCP, Kubeflow Pipelines creates a Google Compute Engine Persistent Disk (PD) and mounts it as a PV.
After deploying Kubeflow on GCP, you can see two entries in the GCP Deployment Manager, one for the cluster deployment and one for the storage deployment:
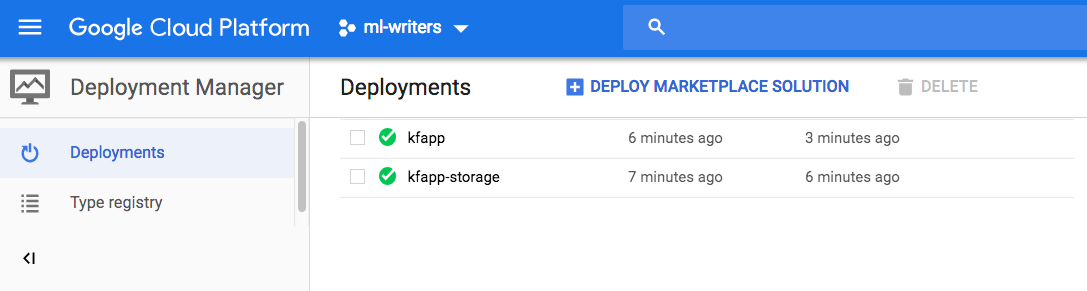
The entry with the suffix -storage creates one PD for the metadata store and
one for the artifact store:
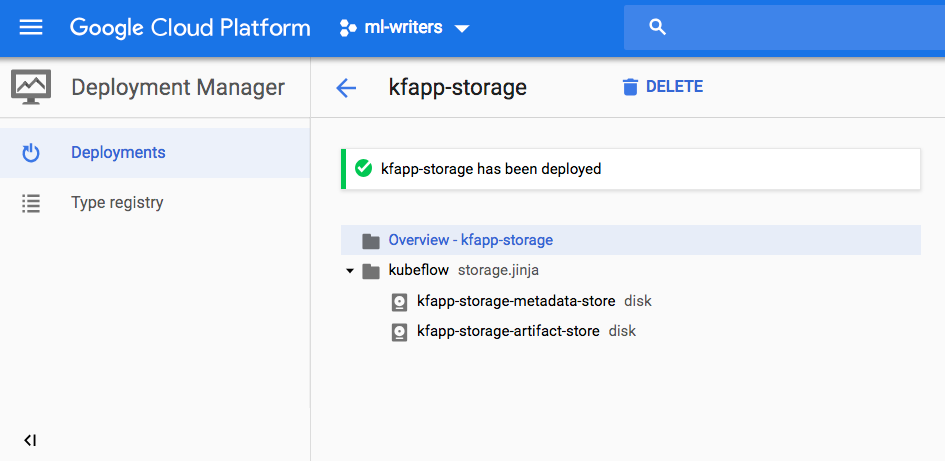
Reinstalling Kubeflow Pipelines
You can delete a Kubeflow cluster and create a new one, specifying your existing storage to retrieve the original data in the new cluster.
Notes:
- You must use command-line deployment. You cannot reinstall Kubeflow Pipelines using the web interface.
- When you do
kfctl applyorkfctl build, you should use a different deployment name from your existing deployment name. Otherwise, kfctl will delete your data in the existing PDs. This guide defines the deployment name in the ${KF_NAME} environment variable.
To reinstall Kubeflow Pipelines:
-
Follow the command-line deployment instructions, but note the following changes in the procedure.
-
Set a different
${KF_NAME}name from your existing${KF_NAME}. -
Before running the
kfctl applycommand:-
Edit
${KF_DIR}/gcp_config/storage-kubeflow.yamland set the following flag to skip creating new storage:... createPipelinePersistentStorage: false ... -
Edit
${KF_DIR}/kustomize/minio/overlays/minioPd/params.envand specify the PD that your existing deployment uses for the Minio server:... minioPd=[NAME-OF-ARTIFACT-STORAGE-DISK] ... -
Edit
${KF_DIR}/kustomize/mysql/overlays/mysqlPd/params.envand specify the PD that your existing deployment uses for the MySQL database:... mysqlPd=[NAME-OF-METADATA-STORAGE-DISK] ...
-
-
Run the
kfctl applycommand to deploy Kubeflow as usual:kfctl apply -V -f ${CONFIG_FILE}
You should now have a new Kubeflow deployment that uses the same pipelines data storage as your previous deployment. Follow the steps in the deployment guide to check your deployment.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Glad to hear it! Please tell us how we can improve.
Sorry to hear that. Please tell us how we can improve.